How To Identify Phosphorus Nutrient Deficiency In Plants
Phosphorus is a vital nutrient for plant growth and development, playing a crucial role in energy transfer, root development, and overall plant health. However, phosphorus deficiencies can hinder plant growth and lead to various symptoms. Identifying these deficiencies early on is crucial for providing the necessary corrective measures.
Definition of Phosphorus
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plants, playing a critical role in growth and development. It helps plants build strong roots and stems, drawing energy from starches and sugars that are created during photosynthesis.
Phosphorus is also important for flowering and fruiting, as it helps facilitate the transfer of energy from one plant part to another. A phosphorus deficiency in plants can be identified by stunted growth, poor root development, a decrease in flowering or fruiting, and yellowing of the leaves.
Without adequate amounts of phosphorus, plants will not be able to produce enough food to sustain healthy growth. To prevent a phosphorus deficiency in your garden or farm, make sure you are using high-quality fertilizer with adequate amounts of this nutrient.
Role of Phosphorus in Plant Growth
Phosphorus plays an important role in plant growth and development. It acts as a catalyst for the production of energy-rich molecules such as ATP and helps in the synthesis of proteins and other essential compounds.
It also helps plants to absorb and utilize other essential nutrients like nitrogen, sulfur, potassium, and magnesium. Phosphorus is vital for photosynthesis, respiration, cell division, root growth, flowering, fruiting, stress tolerance, seed germination, and many other processes.
Without adequate phosphorus levels in the soil, plants may experience stunted growth or underdeveloped root systems which can lead to a decrease in fruits or flowers. Therefore it is important to ensure that your soil has adequate levels of phosphorus for optimal growth of your plants.
Visual Symptoms of Phosphorus Deficiency
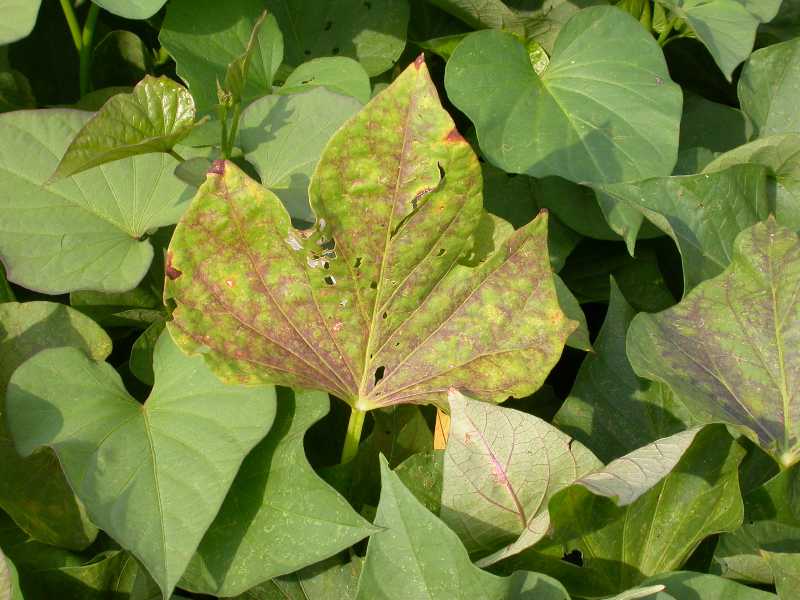
Visual symptoms of phosphorus deficiency in plants include stunted growth, dark green leaves, and yellowing of the lower leaves. The oldest foliage (lower leaves) will be the first to experience a yellow discoloration between the veins. This is due to a lack of cell division and photosynthesis which is caused by inadequate phosphorus levels in the soil.
Additionally, the plant may display slow growth, or even cease growing altogether. Plants with this deficiency may produce fewer flowers and fruits than normal. If you notice any of these signs in your plants it might indicate a phosphorus deficiency so it is important to investigate further and take steps to rectify it.
Leaf Tips & Margins
Leaf tips and margins are important indicators of a phosphorus deficiency in plants. When observing these features, look for signs such as blunting of the leaf’s tips and edges, necrotic spots near the margins, and wilting of the leaves.
These symptoms can be seen on newly developing leaves or on older foliage that has been exposed to prolonged phosphorus deficiency. The yellowing between veins that often occurs with phosphorus deficiency will also be evident on the tips and margins of the leaves.
If any of these symptoms are present in your plants it is important to take further steps to check for phosphorus levels in the soil and remedy them if necessary. By taking action quickly you can help prevent further damage to your plant's growth and health as well as ensure its full potential is realized.
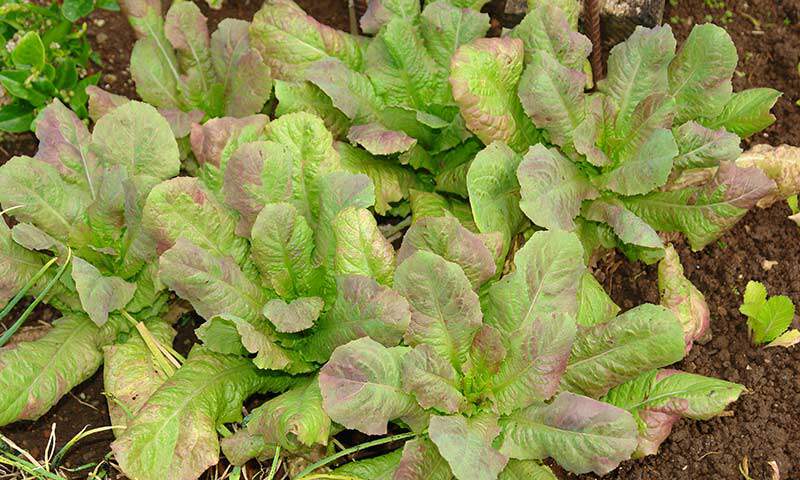
Dark Green Leaves
Dark green leaves are a sign of healthy growth in plants. They indicate that the plant is getting plenty of nutrients and light. However, if leaves become too dark green, this could be a sign that too much nitrogen is being used in the soil. Too much nitrogen can cause the plant to grow rapidly but with little strength which will result in weak stems, poor flowering, and fewer fruits or vegetables.
To identify if your plant has an excess of nitrogen, look for signs such as darker-than-normal leaves and drooping branches. In addition, you may notice yellowing between the veins on the leaves or an overall lack of vigor in the plant's growth.
If these symptoms are present, it is important to test your soil for nitrogen levels and adjust accordingly by adding phosphorus-rich fertilizer or reducing the amount of nitrogen applied to your garden beds. Taking action quickly will help ensure your plants reach their full potential.
Leaf Sizes & Shapes
Leaf sizes and shapes can tell us a lot about the overall health of a plant. Smaller than normal leaves, for example, could indicate a nutrient deficiency such as nitrogen, phosphorus or iron. Such deficiencies can cause the leaves to become stunted and discolored.
On the other hand, larger leaves might be caused by too much water or fertilizer in the soil which can lead to rapid growth but with weak stems and less fruit production.
The shape of a plant's leaves can also give clues about its health. If the edges of the leaves are cupped or rolled inward, this may be a sign that your plant is getting too much sun and needs more shade. If, however, the edges are pointed up toward the sky they may need more sunlight.
Additionally, if you notice holes in your plant's foliage it could mean that there are pests present in your garden which should be addressed quickly to ensure optimal growth.
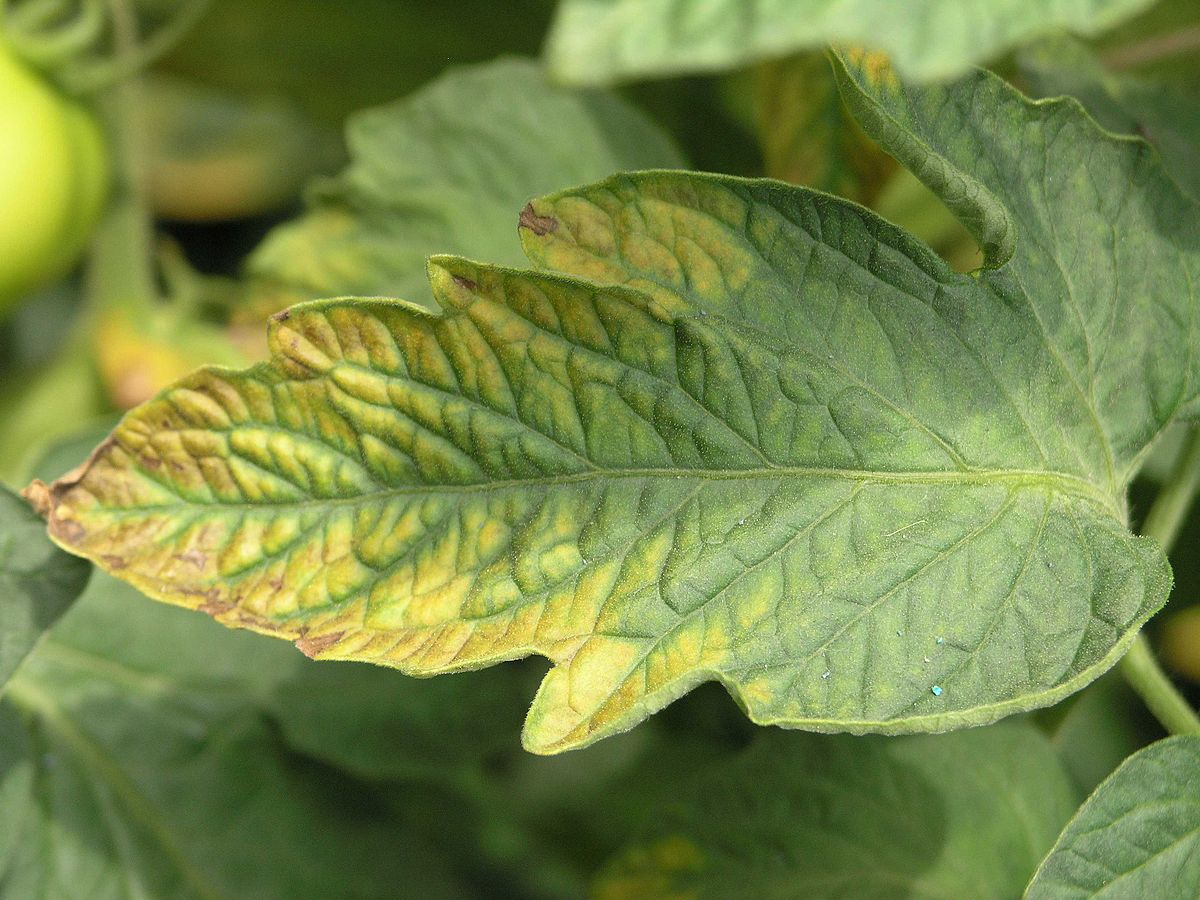
Yellow Leaves
Yellow leaves are one of the first signs that something is wrong with your plants. If you notice your foliage turning yellow, it could be a sign of an underlying nutrient deficiency or disease. It is important to identify the cause in order to address the issue and restore the plant’s health.
Nutrient deficiencies such as nitrogen, phosphorus or iron can cause yellowing leaves. Make sure to check soil pH levels and supplement fertilizer accordingly if needed. Additionally, overwatering or underwatering can also lead to nutrients deficiencies causing yellow leaves. Keep an eye on soil moisture levels and adjust watering frequency as necessary.
Pests or diseases can also cause leaves to turn yellow. Check for signs of aphids or other pests, or for fungal infections such as powdery mildew. Treat any infestations right away before they spread to other plants in your garden.
Stunted Growth
Stunted growth is a telltale sign of nutrient deficiency in plants. If you notice that your plants are not growing as they should, it could be a sign of an underlying problem. Low levels of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus or iron can lead to stunted growth.
Additionally, if the pH level of the soil is too high or low, it can inhibit the plant from absorbing essential nutrients and result in stunted growth.
In order to address this issue, first check the soil pH and supplement fertilizer accordingly if needed. Additionally, make sure you are providing your plants with enough water and sunlight for optimal growth. Too little water or too much shade can also lead to stunted growth.
Finally, keep an eye out for pests or diseases that may be hindering your plants’ growth. Treat any infestations immediately before they spread to other plants in your garden.
Factors Influencing Availability of Phosphorus in Soil
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for healthy plant growth, but availability of this nutrient can vary in different soils. Factors that influence the availability of phosphorus in soil include pH level, organic matter, soil temperature and moisture levels.
Low pH soils have less available phosphorus, as it becomes fixed due to aluminum or iron compounds. High pH soils can also cause phosphorus to become insoluble. Organic matter helps make phosphorus more available by aiding in the release of nutrients from mineral particles. Soil temperature affects the rate at which microbes break down organic matter, releasing additional nutrients into the soil.
Finally, adequate moisture is necessary for sufficient uptake of phosphorus by plants’ roots. By understanding these factors and how they affect availability of phosphorus in soil, gardeners can provide their plants with optimal nutrition for healthy growth.
Plant Species Present
The types of plants that are present in a given environment can depend on a variety of factors, including the availability of phosphorus nutrients. Some plant species are more efficient at taking up phosphorus from soil, while others require higher levels of this essential nutrient to grow and thrive.
Plants that are better adapted to soils with low levels of phosphorus include legumes, grasses, and some fruit trees. On the other hand, plants such as corn and potatoes require more phosphorus for optimal growth.
Additionally, crops that are heavily fertilized will typically have higher phosphorus requirements than those grown in unfertilized soil. By selecting appropriate plant species for our gardens based on the available phosphorus levels in our soils, we can maximize our yields while minimizing nutrient runoff into nearby bodies of water.
Soil pH Levels
Soil pH is an important factor in determining the availability of phosphorus to plants. Soils with a pH below 7 are considered acidic, while those with a pH above 7 are alkaline. In acidic soils, the phosphorus within the soil is less available to plants due to its increased binding to other elements such as aluminum and iron.
As a result, plants grown in acidic soils may be deficient in phosphorus even when adequate amounts of this nutrient are present. To ensure optimal plant growth and production, gardeners should test their soil’s pH levels and adjust accordingly by adding lime to alkalize or sulfur to acidify. By doing so, we can ensure that our plants have access to all the nutrients they need for optimal growth and yield.
Sandy or Calcareous Soils
Sandy or Calcareous soils are those that contain high levels of calcium carbonate. These soils can be found in many parts of the world, and they often require special care to ensure that plants grown in them get the nutrition they need.
Sandy soils or Calcareous soils tend to have a very low pH level, which limits the availability of phosphorus and other essential plant nutrients. To combat this deficiency, gardeners must adjust the soil’s pH level by adding lime or sulfur to make it more acidic or alkaline respectively.
Additionally, adding organic matter such as compost can help improve soil fertility and nutrient availability. By taking these steps, we can ensure that our plants receive all the nutrients they need for optimal growth and yield.
Soil Compaction
Soil compaction is a common problem in agricultural and urban areas, caused by the heavy traffic of vehicles on the land. This compaction reduces soil porosity, which reduces air and water movement through the soil, leading to poor plant growth and decreased yields.
To help prevent soil compaction, farmers should avoid driving on wet soils and use equipment with low ground pressure. Additionally, they can use aeration methods such as deep plowing or subsoiling to loosen compacted soils and improve drainage.
Finally, adding organic matter such as compost or mulch can help break up compacted soils and improve fertility. By taking these steps, we can ensure that our plants receive all the nutrients they need for optimal growth and yield.
Summary
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plant growth, and it is important to ensure that plants are receiving the proper amount. Preventing phosphorous deficiency can be done through the use of quality fertilizers containing all macronutrients (NPK), avoiding over-fertilization with nitrogen fertilizer, and monitoring soil nutrient content annually.
Additionally, adding organic matter to the soil such as compost or manure can help increase water penetration and make phosphorous more available. Taking these steps will ensure healthy plant growth and maximum yields.