Calcium Deficiencies in Plants
Calcium is an essential nutrient vital to plant health, often overlooked in garden care. Deprived of adequate calcium, plants can't reach their full potential, displaying symptoms of deficiency such as stunted growth and brown spots. Understanding the role of calcium in plant life, recognizing the telltale signs of deficiency, and knowing how to correct these deficiencies are crucial for every gardener. Dive into the fascinating world of plant nutrients, focusing on the importance of calcium.
What is Calcium?
Calcium is an essential nutrient for the optimal health and growth of plants. It plays a critical role in various physiological processes, making it a vital element for plant development. One of its primary functions is in the structure of cell walls, where calcium acts as a cementing agent, providing strength and stability. Additionally, calcium has a regulatory effect on plant cells, contributing to healthy growth and development.
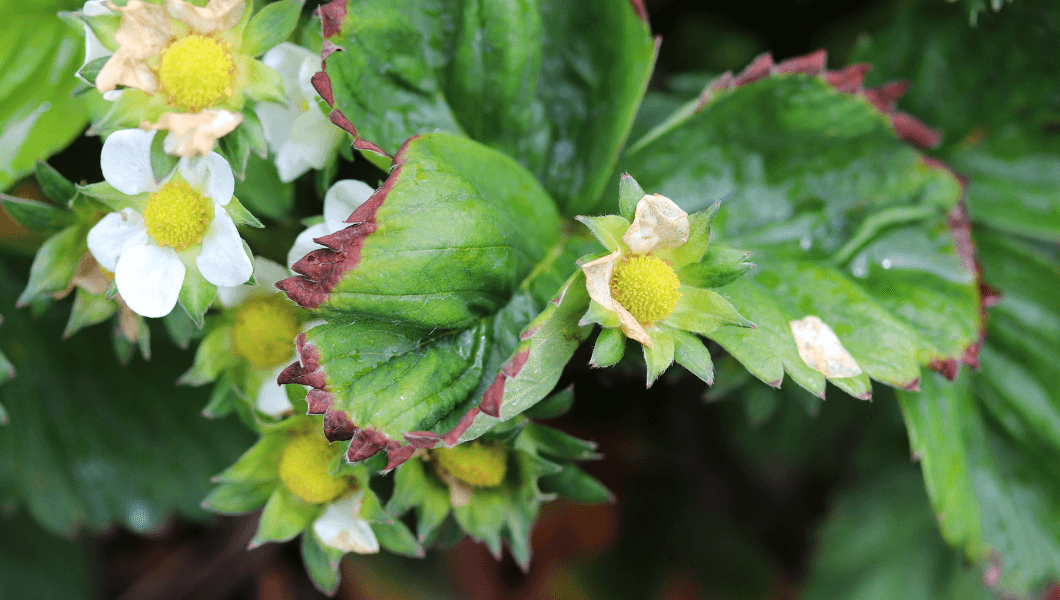
A deficiency in calcium can have detrimental effects on plants, leading to various signs and symptoms. The most common symptom is the appearance of brown or dead spots on leaf surfaces, particularly on the margins. Calcium deficiency can also result in stunted growth, as it affects the transport of other essential nutrients within the plant. This immobile nutrient cannot move easily within the plant, making it crucial for a steady supply of calcium in the nutrient solution.
What Role Does Calcium Play in Hydroponic Plant Growth?
Calcium plays a crucial role in hydroponic plant growth, contributing to the development of strong cell walls, membrane stability, and overall plant structure. As an essential nutrient, calcium is responsible for facilitating proper cell wall formation, which ensures the structural integrity of plant tissues.
In hydroponic systems, where plants obtain their nutrients from a water-based solution instead of soil, calcium deficiencies can have detrimental effects on plant growth. As plants uptake water and nutrients through their root system, a lack of calcium in the nutrient solution can inhibit the development of healthy cell walls. This deficiency manifests as various symptoms, including stunted growth, leaf tip dieback, and distorted leaf margins.
Signs and Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency
Calcium deficiency can lead to various signs and symptoms in hydroponic plants. In severe cases of calcium deficiency, the plants may exhibit stunted growth, as the nutrient deficiency affects their overall development. It is important to address calcium deficiencies in hydroponic plants to ensure optimal growth and productivity.
Leaf Tips and Margins
Calcium deficiency in hydroponic plants can manifest in various ways, including signs and symptoms that affect the leaf tips and margins. One noticeable indication of calcium deficiency is the browning of leaf tips, which may progress towards the center of the leaf. In severe cases, the leaf margins may also exhibit similar symptoms. Additionally, the affected areas may become brittle and prone to cracking.
Furthermore, the root tips play a crucial role in identifying calcium deficiency. Browning, dying off, and blackening of the root tips are common signs of insufficient calcium levels. These symptoms can lead to compromised root health and reduced nutrient uptake, ultimately impacting overall plant growth and development.
Several factors can contribute to calcium deficiency in hydroponic plants. Insufficient calcium levels in nutrient solutions and acidic soil pH levels are significant causes. Calcium, being an immobile nutrient, depends on transpiration rates and environmental conditions to move effectively within the plant. When calcium absorption and transport are hindered, plants may experience a lack of calcium, resulting in deficiency symptoms.
Leaf Surfaces
Calcium deficiency can have detrimental effects on leaf surfaces in hydroponic plants. The lack of calcium can lead to various visual symptoms and characteristics on the leaves, such as discoloration, wilting, and the development of necrotic spots.
One of the most common signs of calcium deficiency on leaf surfaces is the appearance of brown spots. These spots may start small but can eventually spread and cover larger areas of the leaf. In severe cases, the brown spots can turn into dead spots, leading to the death of the affected leaf tissues.
In addition to brown spots, calcium deficiency can also cause deformities in the leaves. The leaves may become misshapen, distorted, or exhibit irregular growth patterns. This can significantly impair the overall health and growth of the plant.
Calcium plays a vital role in maintaining healthy leaf structures and functions in hydroponic plants. It is responsible for strengthening cell walls, regulating cell division, and mediating various metabolic processes. Adequate levels of calcium are essential for the proper development and function of leaf tissues.
To prevent calcium deficiency on leaf surfaces, it is crucial to ensure that hydroponic plants receive a sufficient supply of calcium through nutrient solutions. Calcium nitrate and calcium sulfate are commonly used as water-soluble calcium sources in hydroponic systems. Regular monitoring of calcium levels, along with maintaining optimal environmental conditions and transpiration rates, can help prevent and address calcium deficiency symptoms effectively.
Root Tips
Root tips play a crucial role in plant growth, as they are responsible for absorbing essential nutrients and water from the soil. When it comes to calcium deficiency in hydroponic plants, the root tips are often the first to show symptoms.
Calcium deficiency can lead to a variety of symptoms in plants, including stunted growth, leaf margin necrosis, brown spots, and dead spots on plant tissues. These symptoms occur because calcium is an immobile nutrient, meaning it does not easily move within the plant. As a result, it directly affects the growth and health of new tissues, such as the root tips.
The root tips are vital for plants' calcium nutrition, as they are the primary site for calcium absorption and transport. Calcium is essential for maintaining the integrity of cell walls and regulating various physiological processes within the plant. Without sufficient calcium levels, root tip function is compromised, leading to a reduction in calcium uptake and transport to other parts of the plant.
To prevent calcium deficiencies in hydroponic plants, it is important to ensure a sufficient supply of calcium in the nutrient solution. Calcium carbonate, calcium nitrate, and calcium sulfate are commonly used as water-soluble calcium sources. Additionally, maintaining adequate levels of calcium in the root zone is crucial, especially when using tap water with high levels of calcium.
Cell Walls
Calcium plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of cell walls in hydroponic plants. In the absence of soil, where plants naturally derive calcium, it is vital to ensure an adequate supply of this essential nutrient in hydroponic systems.
Cell walls provide rigidity and structure to plant cells, allowing them to maintain their shape and perform functions such as supporting the plant and protecting it from pathogens. Calcium acts as a cementing agent in cell walls, strengthening the overall structure and enhancing its resistance to physical stresses.
A deficiency in calcium can have detrimental effects on cell walls, leading to various symptoms in hydroponic plants. The lack of calcium can disrupt the cross-linking of pectin molecules, resulting in weak or fragile cell walls. As a consequence, plants may exhibit discoloration, curling of leaves, and the death of meristems.
Furthermore, calcium is involved in binding to phospholipids in cell membranes, contributing to their stability. Insufficient calcium levels can compromise membrane integrity, leading to increased permeability to ions and other substances. This imbalance in ion transport can negatively impact vital cell functions and hinder the overall growth and development of hydroponic plants.
Causes of Calcium Deficiency
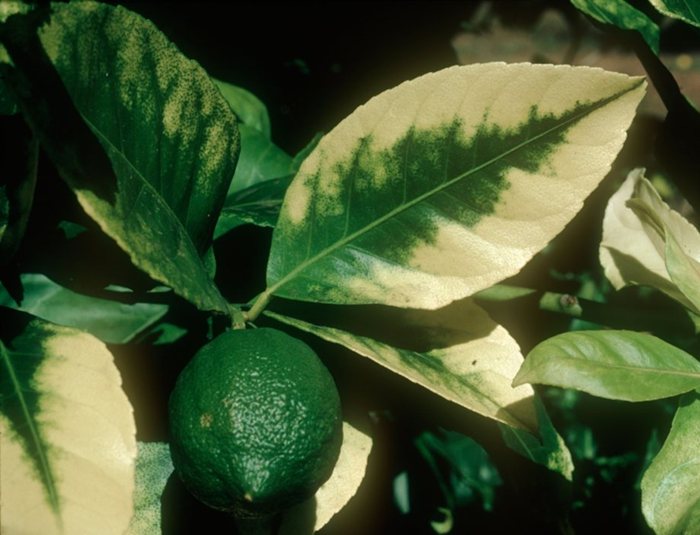

Calcium deficiency is a common nutrient deficiency found in hydroponic plants. Calcium is an essential nutrient for plant growth, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of cell walls. However, hydroponic plants are particularly susceptible to calcium deficiencies due to the absence of natural calcium sources found in soil. The lack of calcium in the nutrient solution can result in reduced calcium uptake by the plant, leading to various deficiency symptoms.
Insufficient Levels of Calcium in Nutrient Solutions
Insufficient levels of calcium in nutrient solutions can negatively impact the growth and development of hydroponic plants. Several factors contribute to calcium deficiencies in hydroponic systems. Firstly, the competitive effects of other nutrients can limit calcium uptake by plants. High concentrations of magnesium, potassium, and ammonium ions can reduce the absorption of calcium.
Additionally, root temperature and water movement play a crucial role in calcium uptake. Cold root temperatures and stagnant water can impede the movement of calcium to the plant's xylem tissue. Conversely, high salinity and humidity levels can also hinder calcium absorption, as they increase water loss through transpiration and reduce the availability of calcium ions.
Maintaining adequate calcium levels in nutrient solutions is essential for plant growth. Higher electrical conductivity (EC) levels in the nutrient solution can decrease calcium uptake. Therefore, it is beneficial to lower the EC at night to enhance calcium absorption. Moreover, reducing nutrient imbalance and adjusting pH levels are key considerations for maintaining sufficient calcium levels. Nutrient imbalances, particularly high levels of potassium and magnesium, should be avoided as they can inhibit calcium uptake.
Low Transpiration Rates
Low transpiration rates in plants can contribute to calcium deficiencies in hydroponic systems. Several factors can cause low transpiration rates, including inadequate water, high humidity, and cold temperatures.
When plants do not receive enough water, their transpiration rates decrease. This affects the movement of water and nutrients, including calcium, through the xylem. The xylem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. With inadequate water, the movement of calcium through the xylem is hindered, resulting in calcium deficiency.
High humidity can also lead to low transpiration rates. When the air is saturated with moisture, plants have a reduced need to transpire and lose water. As a result, the movement of both water and calcium through the xylem slows down, making it difficult for plants to obtain sufficient calcium.
Similarly, cold temperatures can decrease transpiration rates. In colder environments, plants tend to close their stomata, which are tiny openings on the leaf surfaces that regulate transpiration. Closed stomata prevent the loss of water, but they also limit the movement of calcium. As a result, plants may experience calcium deficiencies when exposed to cold temperatures.
Incompatible Environmental Conditions
Incompatible environmental conditions can have a significant impact on the availability and uptake of calcium in hydroponic plants, leading to nutrient deficiencies and hampered plant growth. One of the primary factors contributing to calcium deficiency is excessive acidity or alkalinity in the growing medium. When pH levels deviate from the optimal range of 5.5 to 6.5, calcium may become less soluble and unavailable for absorption by the plant roots.
Another incompatible condition is excess salinity. High levels of salts in the nutrient solution can disrupt the balance of ions in the plant tissues, impeding calcium uptake. Additionally, certain nutrient formulations may not be suitable for specific plant species. Different plants have varying calcium requirements, and if the nutrient solution is not properly formulated to meet these needs, calcium deficiency can occur.
These incompatible conditions negatively affect plant growth by hindering the movement of calcium within the plant. Calcium plays a vital role in cell wall development, strengthening plant structure, and facilitating essential metabolic processes. Calcium deficiencies can manifest as signs such as brown spots on leaf surfaces, dead spots along leaf margins, or tip burn. Without adequate calcium levels, plants may experience reduced transpiration rates, impaired water regulation, and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests.
Lack of Essential Nutrients in the Soil or Media
Addressing the lack of essential nutrients in the soil or grow media is vital when fixing a calcium deficiency in hydroponic plants. Calcium deficiency can occur when there is an absence of necessary nutrients, which are essential for proper plant growth and calcium absorption.
To maintain optimal plant health, it is crucial to ensure that all required nutrients are present in adequate amounts. The key nutrients for proper plant growth and calcium absorption include not only calcium but also nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and others.
Soil testing is an effective method to identify nutrient deficiencies. By analyzing the nutrient content of the soil or media, it becomes possible to identify any lacking nutrients, including calcium. Once the specific deficiencies are identified, appropriate solutions can be implemented to replenish them.
Replenishing the lacking nutrients can be achieved through various ways, such as using nutrient solutions or adding appropriate amendments to the soil or media. For calcium deficiencies, using a water-soluble calcium source, such as calcium nitrate or calcium sulfate, can help increase the level of calcium in the growing medium.
Acidic Soil pH Levels
Acidic soil pH levels can negatively impact calcium absorption in plants. When the pH of the soil becomes too low (acidic), it can cause a reduction in calcium uptake by the plant roots. This is because acidic conditions interfere with the availability and movement of calcium in the soil.
Maintaining an optimal pH range is crucial in hydroponic systems as pH directly affects nutrient availability. In hydroponics, plants rely on nutrient solutions to meet their nutritional needs. The pH of the nutrient solution plays a significant role in determining the availability of essential nutrients, including calcium.
The relationship between pH and nutrient availability is illustrated in the provided chart. As the pH moves away from the optimal range, the availability of nutrients decreases. At extreme acidic pH levels, calcium and other vital nutrients become less accessible to the plant roots, resulting in nutrient deficiencies and related symptoms.
How to Test for Calcium Deficiency in Plants
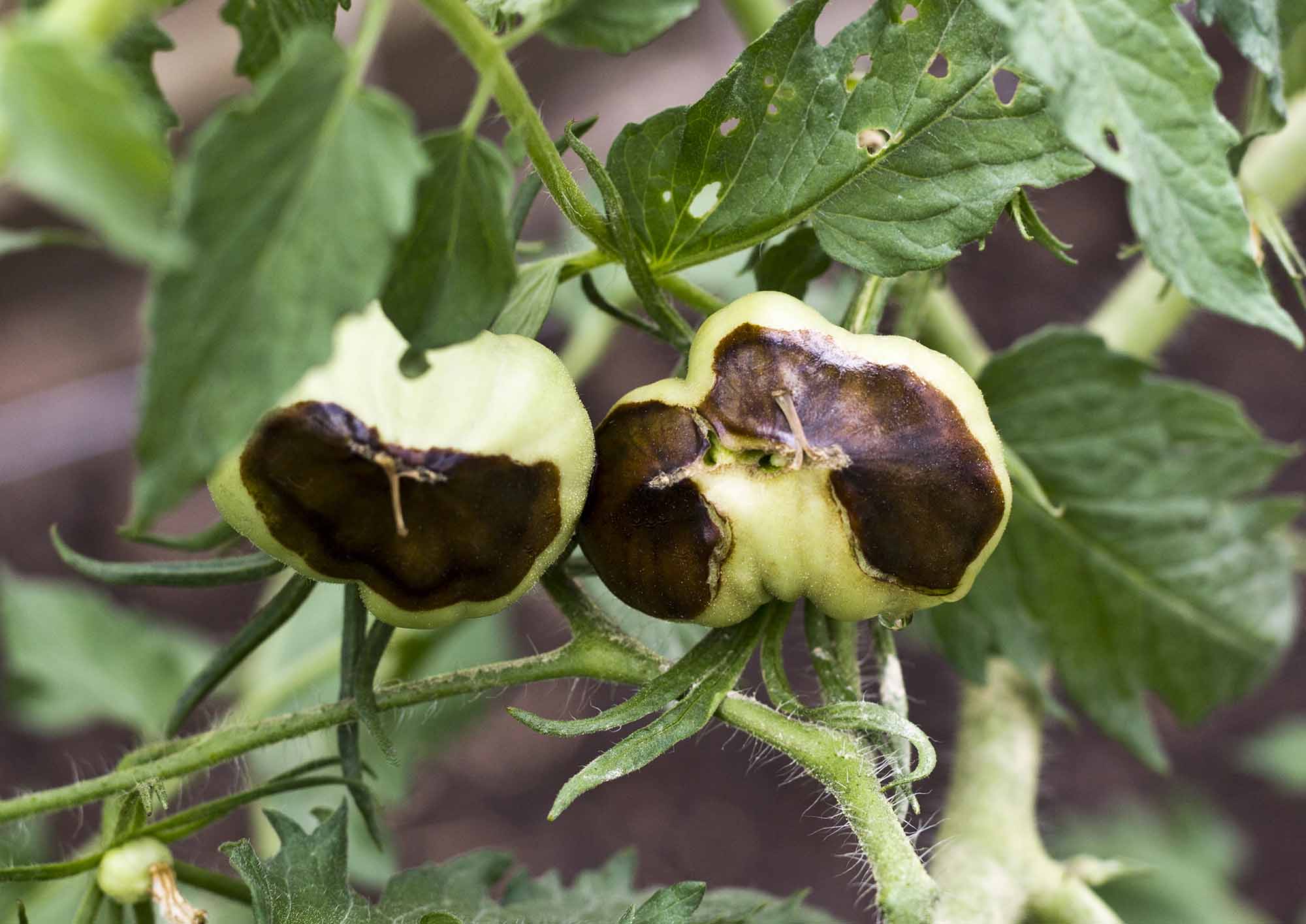

In hydroponic systems, calcium deficiencies can hinder plant growth and development. Identifying and addressing these deficiencies promptly is crucial to maintain healthy plants. Testing and diagnosing calcium deficiency can be done using several methods.
One method is visual inspection. Signs of calcium deficiency can be observed in the plant tissue, particularly in the leaf surfaces and margins. Look out for browning or yellowing of leaf tips, dead spots, or brown spots, as these may be indicative of a lack of calcium. Additionally, plants with calcium deficiencies may exhibit stunted growth and reduced fruit or flower production.
Another method is testing the nutrient solution. By analyzing the nutrient solution used in the hydroponic system, one can determine if adequate levels of calcium are present. Calcium levels in nutrient solutions can be measured using various testing kits or meters.