What is The Difference Between Hydroponics, Aquaponics & Aquaculture?
Imagine a world where plants grow without soil, fish farms produce more than just seafood, and farms function in a harmonious cycle, with each element supporting the other. Sounds fascinating, right? Well, this isn't just a scene from a sci-fi movie; it's happening right here, right now! Welcome to the exhilarating world of Hydroponics, Aquaponics, and Aquaculture – three game-changing methods that are reshaping our understanding of agriculture.
As our planet's population grows and the demand for food skyrockets, these innovative farming practices are not just intriguing buzzwords; they're solutions for a sustainable future! Ready to dive deep and uncover the distinctions and marvels behind each method? Buckle up, because this is one enlightening journey you won't want to miss!
How Do These Systems Differ?
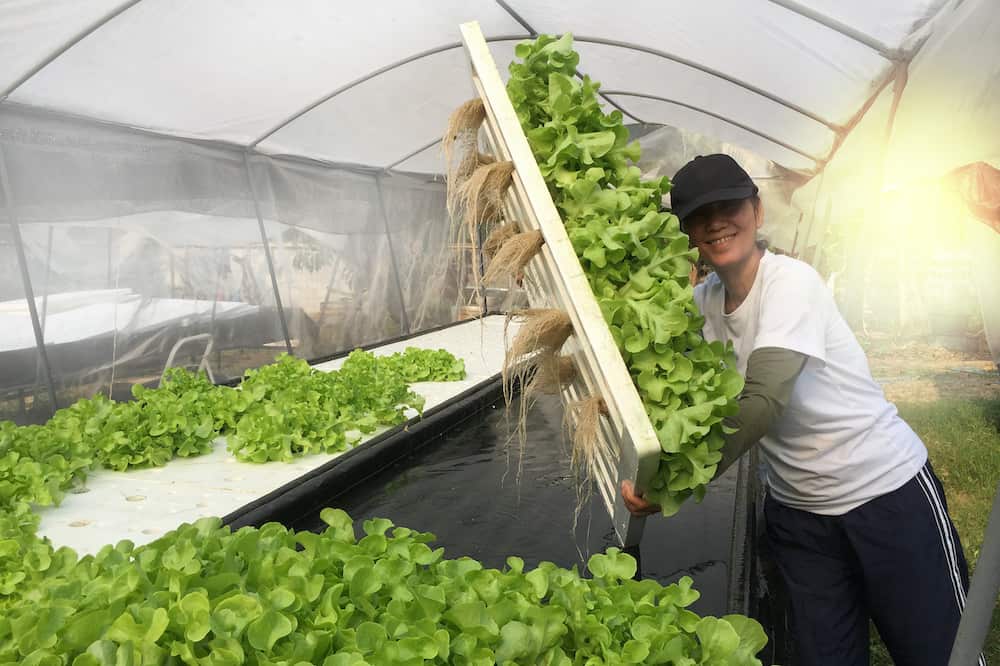

Hydroponics, aquaponics, and aquaculture are all methods of growing plants, but they differ in their approach and the role of fish waste and nutrient solutions.
Hydroponics involves growing plants without soil. Instead, plant roots are suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution that provides all the essential nutrients they need. This system typically relies on water pumps, air stones, and water temperatures to ensure optimal plant growth. Hydroponics is popular for its faster growth and higher nutrient levels, but it requires regular monitoring of nutrient levels and can be susceptible to root rot if not managed carefully.
Aquaponics, on the other hand, combines hydroponics with aquaculture. It utilizes a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. Fish waste provides essential nutrients to the plants, while the plants filter the water for the fish. This system often includes a fish tank, grow bed, and a constant flow of water. Aquaponics is known for its sustainable nature and the ability to grow both leafy greens and aquatic species.
Aquaculture, also known as fish farming, is focused mainly on the cultivation of aquatic species. It involves raising fish in controlled environments and providing them with proper nutrition, typically through fish feed. Aquaculture systems can range from small-scale operations to large commercial setups.
Hydroponic System Overview
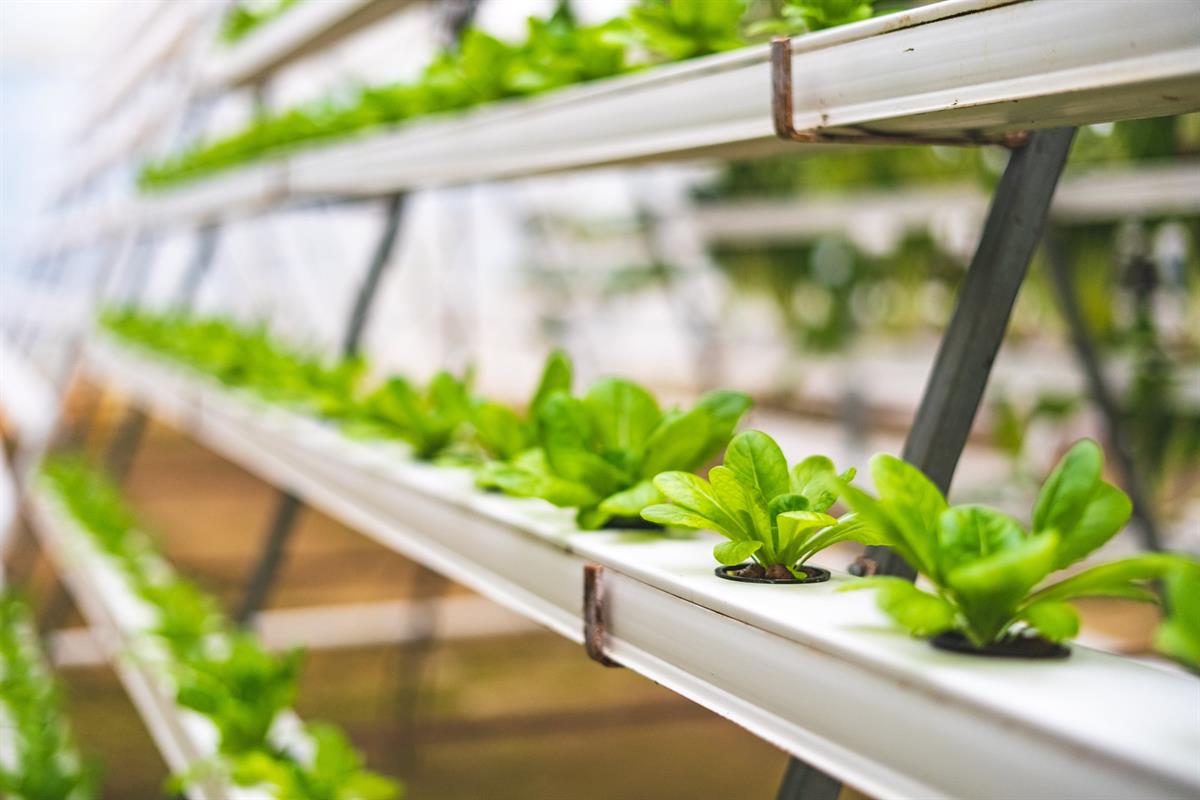

Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, where the plant roots are exposed to a nutrient-rich water solution. This system allows for optimal plant growth as the plants have easy access to the essential nutrients they need. Hydroponic systems typically involve the use of a water tank that holds the nutrient solution and a grow bed where the plants are placed.
Nutrient-Rich Water Supply
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, where the roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich water solution. The key difference between hydroponics and traditional soil gardening lies in the way plants receive their essential nutrients.
In hydroponic systems, a nutrient solution is circulated directly to the plant roots. This allows for precise control over nutrient levels, resulting in faster plant growth and healthier plants. By eliminating soil as a growing medium, hydroponic plants can access nutrients more efficiently, leading to increased plant production.
Maintaining proper nutrient levels is crucial in hydroponic gardening. Commercial growers and hydroponic enthusiasts carefully monitor the nutrient composition of the water to ensure plants receive all the essential nutrients they need. This is achieved by adding chemical nutrients to the water solution, which can be tailored to the specific requirements of different plant species.
The use of a nutrient-rich water supply in hydroponics offers several advantages. It allows for faster growth rates, as plants have constant access to the necessary nutrients. Additionally, hydroponics reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, as plants are grown in a controlled environment. Furthermore, hydroponic systems are more efficient in their water usage compared to traditional soil gardening.
More: How To Grow Hydroponic Plants?
Plants Without Soil
Traditionally, plants have been grown in soil, which provides essential nutrients and support for their growth. However, innovative farming techniques have emerged that allow plants to thrive without soil. This practice, known as soil-less cultivation, involves harnessing alternative growth mediums such as water or inert materials.
One popular method of soil-less cultivation is hydroponics, which utilizes a nutrient-rich water solution to feed plants directly. Hydroponic systems provide the perfect balance of essential nutrients, allowing plants to grow faster and produce higher yields compared to traditional soil gardening. This method also eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases and reduces the environmental impact associated with chemical fertilizers.
Faster Plant Growth
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water as a replacement. This system offers several advantages that contribute to faster plant growth compared to traditional soil gardening.
Firstly, the absence of soil eliminates the risk of root rot and other soil-borne diseases that can hinder plant growth. With hydroponics, plant roots directly absorb water and nutrients from a carefully formulated nutrient solution, providing plants with optimal nutrition and reducing the chances of nutrient deficiencies.
Secondly, hydroponic systems provide a precise nutrient supply to plants. This allows growers to have greater control over nutrient levels, ensuring that plants receive the exact balance of essential nutrients they need for optimal growth. By eliminating variables like soil composition and variability, hydroponic growers can fine-tune nutrient solutions to meet the specific requirements of different plant species, resulting in faster and healthier plant growth.
Lastly, hydroponic systems offer optimized growing conditions. Growers can adjust factors such as water temperatures, air pumps, and water pumps to create the ideal environment for plant growth. This level of control over environmental variables promotes faster plant growth by providing plants with the perfect conditions they need to thrive.
Aquaponic System Overview
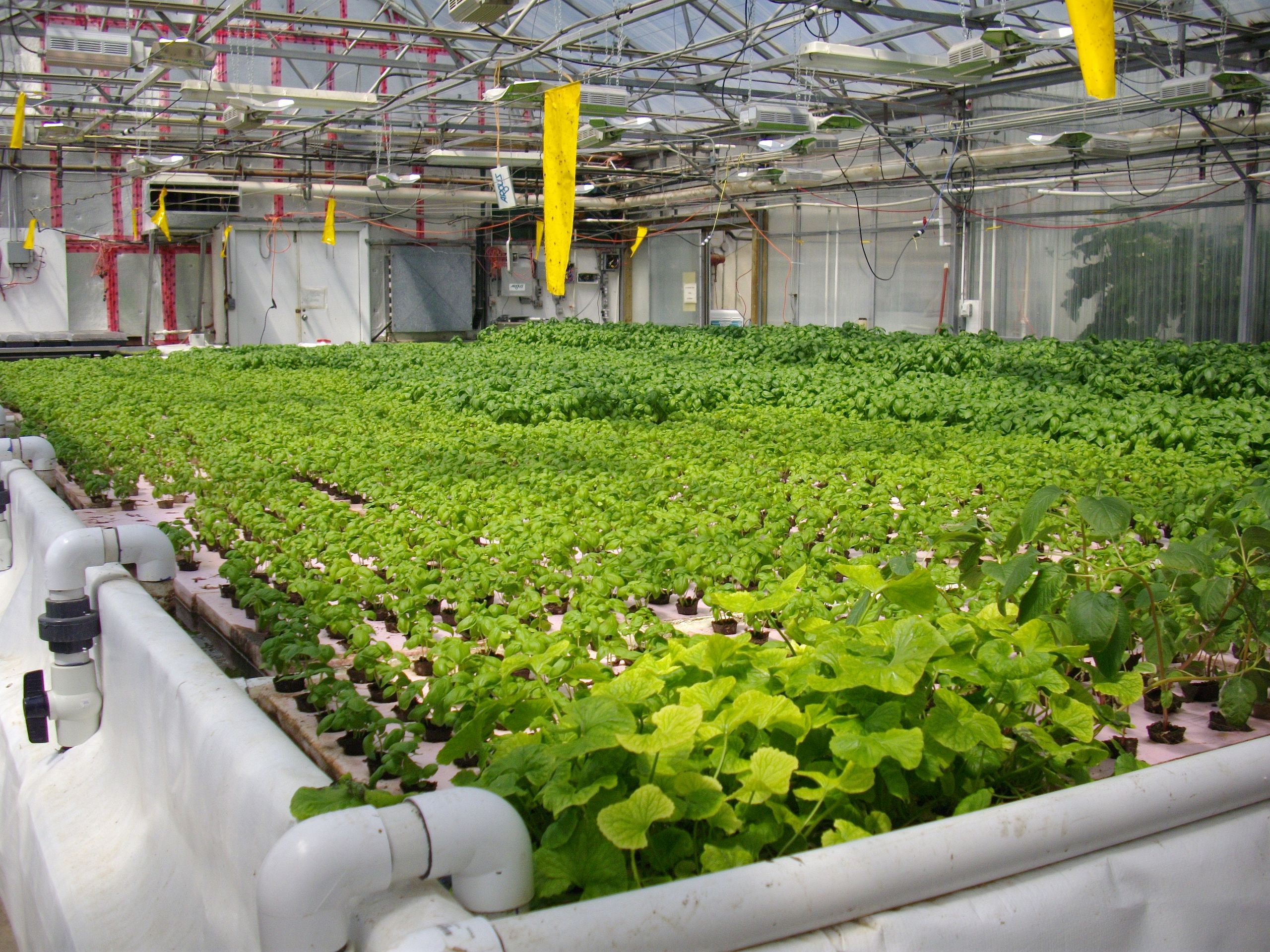

Aquaponics is a unique and sustainable system that combines elements of hydroponics and aquaculture to create a mutually beneficial environment for both plants and fish. In an aquaponic system, plants grow without soil, instead, their roots are submerged in nutrient-rich water. This water is constantly circulated from a fish tank to the plants, providing them with the essential nutrients they need for growth. The fish waste serves as the food source for the plants, as it contains valuable nutrients that plants require. The plants, in turn, act as a natural filter, purifying the water for the fish.
Nutrient Solution for Plants
In both hydroponic and aquaponic systems, the nutrient solution plays a vital role in promoting healthy plant growth. This solution is a combination of water and essential nutrients that are necessary for plant development and maintenance.
Hydroponic systems involve the cultivation of plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution. The roots of the plants are submerged directly in the solution, allowing for faster growth and eliminating the need for traditional soil gardening methods. The nutrient solution provides the plants with all the essential nutrients they require for their growth, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.
Similarly, in aquaponic systems, the nutrient solution is created from fish waste. Aquaponics is a combination of aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics. The nutrient-rich water from the fish tank is pumped into the grow bed where plants are grown. The plants then filter out the waste from the water while absorbing the necessary nutrients, effectively purifying the water for the fish.
The Environmental Impact of Aquaponics
Aquaponics is an innovative and sustainable farming method that combines hydroponics and aquaculture to create a symbiotic ecosystem. This system has a minimal environmental impact and offers numerous advantages over traditional agriculture methods.
Firstly, aquaponics is highly resource-efficient. It requires 90% less water compared to conventional soil gardening, making it an ideal solution for regions facing water scarcity. The closed-loop system recirculates water, eliminating the need for excessive irrigation and reducing overall water usage.
Additionally, aquaponics eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers. In this system, fish waste provides a nutrient-rich solution that is circulated to the plants' root systems. As a result, plants receive all the essential nutrients they need for healthy growth, eliminating the need for chemical additives. This not only minimizes environmental pollution but also promotes organic and sustainable plant production.
Aquaculture System Overview
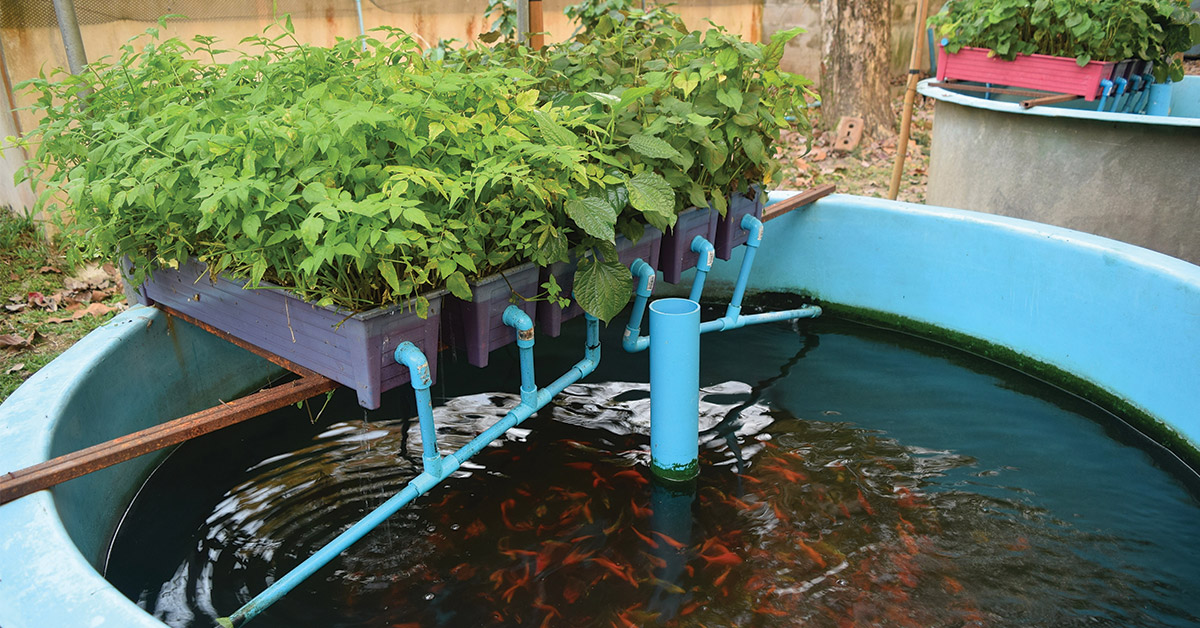

Aquaculture, also known as fish farming, refers to the breeding, rearing, and harvesting of aquatic organisms, such as fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants, in a controlled environment. Unlike hydroponics and aquaponics, which focus on growing of plants, aquaculture concentrates on the production of aquatic species predominantly for human consumption. Aquaculture systems typically involve the use of tanks, ponds, or enclosed areas with controlled water conditions to provide optimal growth conditions for the aquatic organisms. Various techniques, such as feeding the fish with a specially formulated diet, managing water quality, and preventing diseases, are employed to ensure the well-being and healthy growth of the species. Aquaculture plays a crucial role in meeting the increasing demand for seafood and can be practiced on a small scale by individual farmers or on a large scale by commercial operations.
Leafy Greens and Other Plants Grown Together
Leafy greens and other plants can be grown together in aquaponics systems, which is a combination of aquaculture and hydroponics. In aquaponics, fish are raised in a tank and their waste, which contains essential nutrients, is circulated to the grow bed where the plants are cultivated.
The plants, including leafy greens, have their roots suspended in the nutrient-rich water, allowing them to absorb the necessary nutrients without the use of soil. This method promotes efficient nutrient cycling, as the plants take up the fish waste and purify the water for the fish. The plants benefit from the fish waste, while the fish benefit from the purified water.
One of the key benefits of growing leafy greens and other plants together in aquaponics systems is the enhanced plant growth. The plants receive a constant supply of nutrient-rich water, which allows them to grow faster and healthier compared to traditional soil gardening methods. Additionally, the plants in aquaponics systems are less prone to pests and diseases that are associated with soil, resulting in higher plant production.
Comparative Analysis: Hydroponics vs. Aquaponics vs. Aquaculture

Hydroponics, aquaponics, and aquaculture are all methods used in modern agriculture for the production of plants and aquatic organisms. While they share similarities in terms of their use of water and nutrients, there are key differences between them.
Efficiency and Sustainability
Hydroponics, aquaponics, and aquaculture are all innovative systems that offer efficient and sustainable solutions for plant and fish production.
Hydroponics eliminates the need for soil by allowing plants to grow in a nutrient-rich water solution. This method minimizes resource wastage by providing plants with only the necessary nutrients they need for optimal growth. Water and nutrient usage are highly efficient, as the system recirculates the solution, resulting in less water consumption. Additionally, hydroponics maximizes productivity by providing constant access to essential nutrients, promoting faster plant growth.
Aquaponics takes the efficiency of hydroponics a step further by combining hydroponic plant cultivation and aquaculture in a symbiotic environment. In this system, fish waste provides the nutrients for the plants to thrive, while the plants filter the water for the fish. This creates a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and maximizes resource utilization. The efficiency of water usage is significant, as water is constantly recycled and reused, reducing the overall water consumption.
Aquaculture focuses primarily on fish production and is a sustainable alternative to traditional fishing practices. By raising fish in controlled environments, aquaculture limits the depletion of wild fish stocks. Additionally, waste management plays a crucial role in this system, as solid wastes are regularly removed to maintain water quality. Efficient feed management reduces the environmental impact associated with excessive fish feed usage.
Economic Viability
Hydroponics, aquaponics, and aquaculture are all methods of sustainable agriculture that offer economic viability in terms of costs, profitability, and market demand.
Hydroponics involves growing plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution. This system minimizes water usage, reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, and allows for precise control of nutrient levels. Hydroponic plants often have faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional soil gardening. This makes hydroponics a viable option for commercial growers looking to maximize their plant production and profits.
Aquaponics takes hydroponics a step further by combining it with aquaculture, which is the farming of aquatic species. In this system, fish waste from a fish tank provides the nutrients for the plants while the plants filter the water for the fish. By creating a symbiotic relationship, aquaponics eliminates the need for chemical nutrients and offers a sustainable solution for both plant and fish production. The market demand for organically grown produce makes aquaponics commercially viable.
Aquaculture focuses solely on fish farming and has been successfully implemented for commercial operations. With increasing demand for seafood, aquaculture offers an economically viable solution by providing a controlled environment for fish production. The use of proper feeding techniques and water management can reduce the environmental impact associated with traditional fishing methods.
Suitability and Scalability
Hydroponics, aquaponics, and aquaculture are all cultivation methods that offer unique advantages and limitations in terms of suitability and scalability.
Hydroponics is the practice of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water or a nutrient solution. This method is highly suitable for urban environments and areas with limited space, as it requires less space compared to traditional soil gardening. Hydroponic systems can be easily scalable, allowing for larger operations to be established with proper planning. However, this method can be labor-intensive, requiring regular monitoring and maintenance to prevent issues like root rot or nutrient deficiencies.
Aquaponics combines hydroponics with aquaculture, creating a symbiotic relationship between plants and fish. Fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter the water for the fish. Aquaponics is suitable for small to medium-scale operations and is known for its ability to produce leafy greens and herbs effectively. The system can be expanded, but scalability is limited by the size and capacity of the fish tank. Additionally, water temperature and nutrient levels need to be carefully managed to ensure the health of both plants and fish.
Aquaculture involves the farming of aquatic species for food production. It is highly scalable, catering to both small-scale and large-scale commercial growers. Aquaculture systems can be designed to accommodate larger operations by increasing the size and number of fish tanks or ponds. However, this method requires a significant amount of space and resources, including water usage and fish feed. Environmental impact is also a concern, as the concentration of fish waste and chemical fertilizers can lead to waterborne diseases and pollution.
FAQs
What is the main difference between hydroponics, aquaponics, and aquaculture?
The main difference lies in the relationship between plants and aquatic life. Hydroponics involves growing plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution. Aquaponics combines hydroponics with aquaculture, where fish waste provides nutrients to plants. Aquaculture, on the other hand, focuses solely on the farming of aquatic species.
How do plants obtain nutrients in a hydroponic system?
In a hydroponic system, plant roots are submerged or exposed to a nutrient solution that contains essential nutrients. The plant roots directly absorb these nutrients, allowing for efficient and targeted nutrient uptake.
What are the advantages of aquaponics over traditional farming methods?
Aquaponics offers several advantages over traditional farming methods. First, it is an environmentally friendly system as it minimizes water usage and eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers. Second, the combination of aquaculture and hydroponics creates a symbiotic relationship where fish waste becomes a valuable nutrient source for plants. Lastly, aquaponics can produce both fish and plants simultaneously, maximizing food production in limited space.
Are there any differences in plant growth between hydroponics and aquaponics?
Both hydroponics and aquaponics provide optimal conditions for plant growth. However, aquaponics offers additional benefits. The fish waste in aquaponics systems provides a continuous supply of nutrients, resulting in faster plant growth and higher nutrient levels in comparison to traditional hydroponic systems.
How does aquaculture differ from aquaponics?
While both aquaculture and aquaponics involve the breeding and cultivation of aquatic species, there is a key difference. Aquaculture solely focuses on fish farming, aiming to maximize fish production. In contrast, aquaponics integrates fish farming and hydroponics, combining the benefits of both to create a sustainable and symbiotic system.