How To Measure Grow Light With A Par Meter
Optimizing your indoor garden's light conditions is essential for plant health and productivity. One reliable method involves using a PAR meter to measure grow light intensity. This guide will provide a step-by-step tutorial on how to effectively measure your grow light with a PAR meter, ensuring your plants thrive in an ideal light environment.
Why Use a Par Meter to Measure Grow Light?
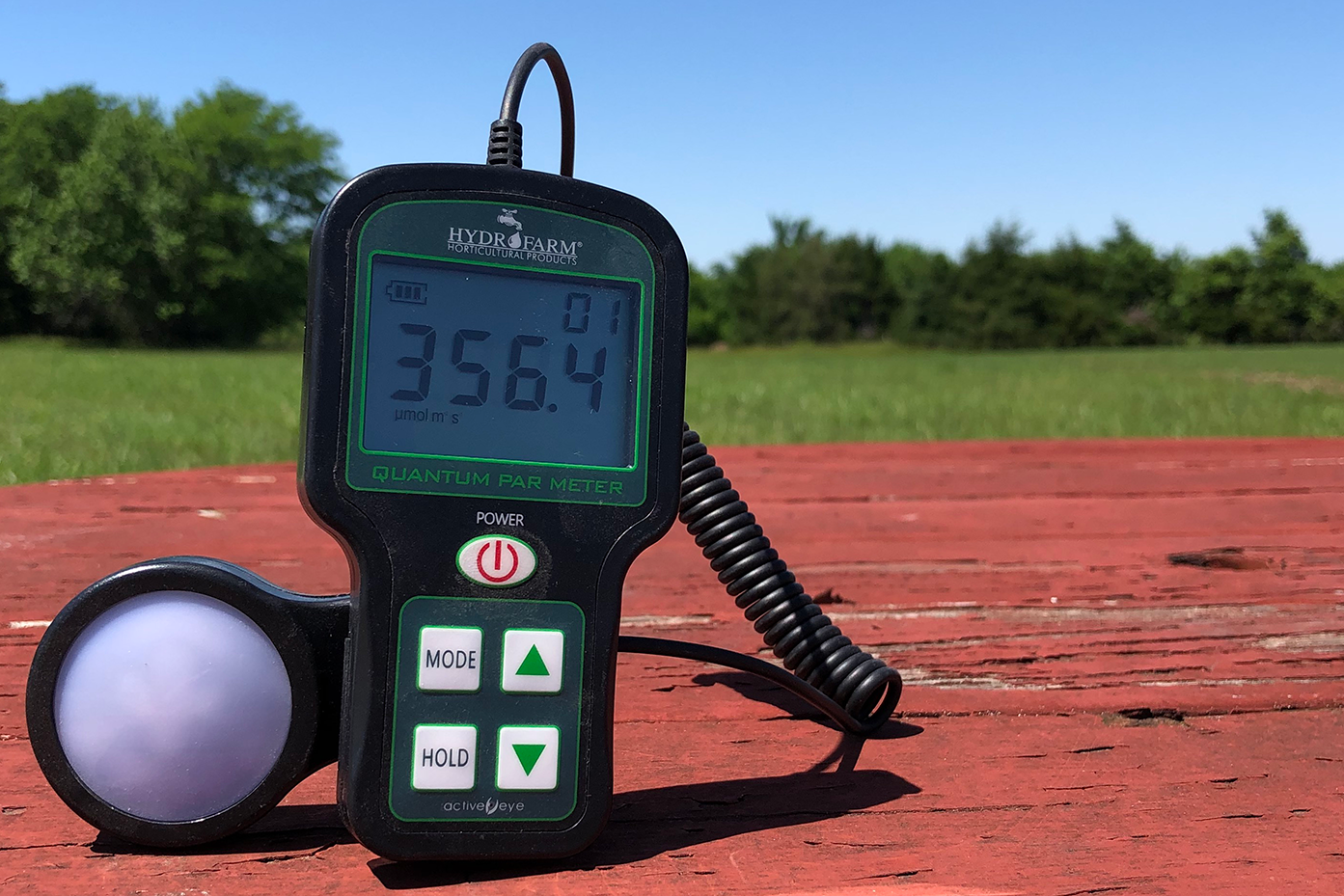
A PAR meter (Photosynthetically Active Radiation) is a device used to measure the intensity and spectrum of the light that is useful for plant growth. It measures light in the range of 400-700nm, which is the photosynthetically active range of light (PAR). By measuring this range of light, a PAR meter can provide accurate readings of the intensity and quality of light that plants need for optimal growth and development.
Using a PAR meter offers many benefits to indoor gardeners. First, it allows them to monitor light levels and optimize lighting conditions to ensure that plants receive the right amount of light for their growth. This is especially important because plants grow differently depending on the amount and quality of the light they receive.
Steps to Determine Grow Light Intensity Using a PAR Meter
One way to determine whether your plants are getting enough light is by using a PAR meter. A PAR meter measures the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) emitted by artificial light sources, which is vital for plant growth.
Step 1: Establish the Light Source and Fixture
To effectively measure grow light with a PAR meter, the first step is to establish the light source and fixture in the grow space. Examining the recommended hanging height, coverage area, and PAR value provided by the lighting manufacturer is crucial in choosing the appropriate lighting for the plants being grown.
It is important to take into consideration the size of the grow space and the specific needs of the plants as different plants may require different levels of light intensity. Once the required specifications are identified, choose a suitable light fixture and ensure that it is securely installed in the grow space.
Before taking measurements using a PAR meter, test the functionality of the light fixture to ensure that it is emitting the desired amount of PAR. Proper testing can assist in avoiding any complications in the measurement process.
Step 2: Calculate the Daily Light Integral (DLI) and Usable Light per Square Meter (UL/M2)
When it comes to growing plants indoors, one of the most crucial aspects to monitor is the amount of light your plants receive. This is where measuring Daily Light Integral (DLI) and Usable Light per Square Meter (UL/M2) comes into play. DLI is a measure of the total light energy received by your plants every day, while UL/M2 is a measure of the amount of usable light per square meter. By measuring both DLI and UL/M2, you can ensure that your plants are receiving enough light to support healthy growth and photosynthesis.
To calculate DLI, you will need to measure the Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density (PPFD) at different points throughout the day and sum those values. PPFD is the amount of PAR (Photosynthetic Active Radiation) received by a plant per second, and it is measured in micromoles per meter squared per second (µmol/m²/s).
To measure PPFD, you will need a quantum sensor or a PAR meter. It is recommended to take measurements at least 3-4 times a day, including at the beginning and end of the light cycle, to get an accurate reading of the total light energy received by your plants. Once you have the PPFD values for each measurement, you can add them up to get the total DLI.
For UL/M2, you will need to measure the PPFD at each point inside the grow tent and then divide that number by the area of the tent to get the average PPFD per square meter. This can be done by taking multiple readings at different points inside the tent and then averaging them. Once you have the average PPFD per square meter, you can use this value to calculate the UL/M2.
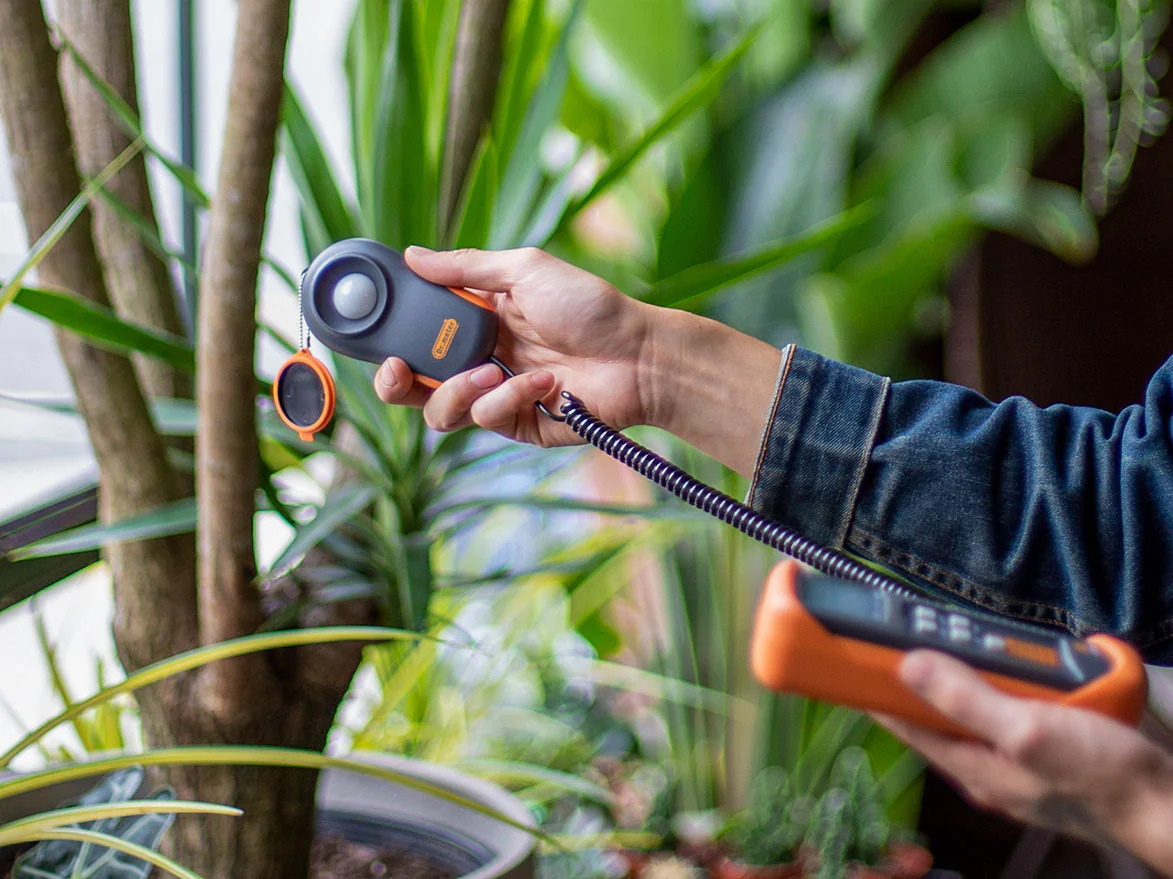
Step 3: Set Up Your Par Meter and Quantum Sensor
Once you have selected the right PAR meter and quantum sensor for your grow light, it's time to set them up to begin measuring the light intensity. Here's how to get started:
- 1. Set up PAR meter:
The first step is to set up your PAR meter according to the manufacturer's instructions. Make sure the battery is fully charged before use. Also, take the time to familiarize yourself with the device and its various features.
- 2. Connect sensor:
Next, you will need to connect the sensor to your PAR meter. Most PAR meters come equipped with a jack that connects to your sensor. Once you have connected the sensor, you should switch on your meter and begin taking readings.
- 3. Proper placement:
The placement of your quantum sensor is essential for obtaining accurate readings. You will need to position the sensor in the middle of the plant canopy, about 6-12 inches away from the light source, and directly under the center of the light fixture. Make sure the sensor is not obstructed by any leaves or foliage.
- 4. Calibration process:
Before taking any measurements, you should calibrate your PAR meter and quantum sensor to ensure accuracy. The calibration process will vary depending on the manufacturer's instructions, so be sure to consult the user manual carefully.
Step 4: Take Measurements of Plant Canopy, Plant Growth, and Sun Systems
When it comes to measuring grow light with a PAR meter, it is important to take accurate measurements of the plant canopy, plant growth, and sun systems. These measurements will help you understand how the plants are responding to the light and make any necessary adjustments to improve their growth.
Firstly, when measuring the plant canopy, there are a few aspects to consider. You will need to measure the height and width of the plant, as well as the density of the leaves. This will enable you to understand how much light the plant is receiving and whether it is being distributed evenly across the plant. Additionally, if you identify any areas of the plant where light is insufficient, you can make adjustments to your light fixtures to ensure that all parts of the plant are receiving adequate light.
Secondly, monitoring plant growth is crucial to understand how the plant is responding to the light. You can measure the height of the plant and the distance between the nodes (internodal spacing) to get an idea of how the plant is growing. Also, observing the size of the leaves will help you determine the effectiveness of the light on the plant's growth.
Thirdly, when measuring sun systems, there are many factors to consider. You need to measure the distance from the light source to the plant, the direction of the light, and the orientation of the light fixture. These will all affect the intensity and distribution of light that the plant receives. Taking accurate measurements will help you determine the most effective placement of the grow light and ensure that the plant receives the proper amount of light.
Step 5: Record Lux Level, Quantum Outputs, and Spectral Range Readings
When measuring grow light with a PAR meter, it's essential to record the lux level, quantum outputs, and spectral range readings. Lux level measures the intensity of light visible to the human eye, while quantum output is a measure of the amount of photosynthetically active light available for plants to use for growth.
Spectral range readings are also crucial as they indicate the specific wavelengths of light emitted by the grow light. Different plants require different wavelengths of light to grow, and it's essential to ensure that the grow light provides the necessary wavelengths for optimal plant growth.
To record these measurements, place the PAR meter and quantum sensor at the same height as the plant canopy. Position the quantum sensor in the center of the plant canopy and record the readings provided by the PAR meter.
Step 6: Check for Consistency in Metering Readings
Slight variations in meter readings can occur due to factors such as temperature, distance, or lighting conditions. Therefore, it is essential to check for consistency in metering readings to ensure accurate results.
One way to do this is to take multiple measurements at various points within the plant canopy and compare the average values. This method helps to identify any significant disparity in meter readings for different parts of the plant canopy. By taking multiple readings and calculating the average, a more reliable measurement of the intensity of light is obtained.
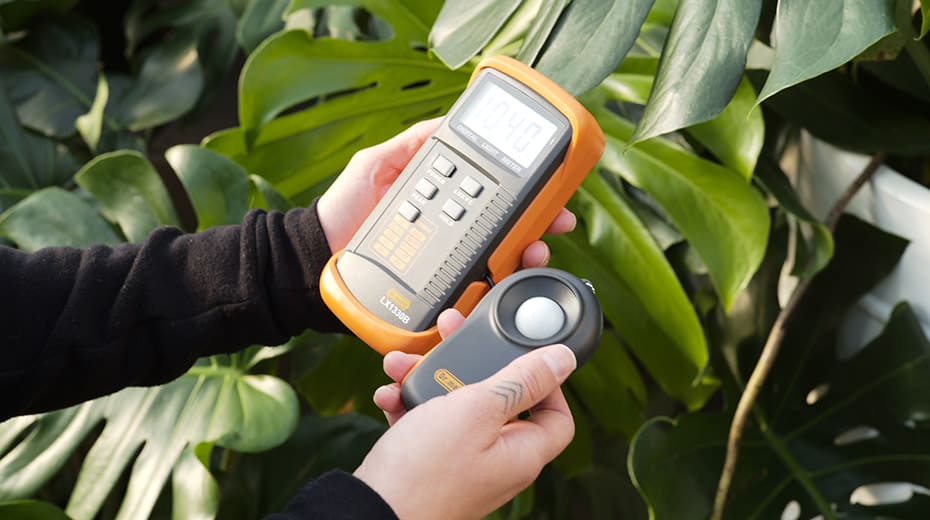
Another way to check for consistency is to repeat the measurement process using a different PAR meter or quantum sensor to cross-reference the results. When using a different PAR meter, it is essential to calibrate the device to ensure it is providing readings that are as accurate as possible.
Step 7: Adjust Lighting as Needed Based on Results
Once you have taken accurate readings using the PAR meter, it is time to analyze and evaluate the data. This will help you to determine if any adjustments are needed in the lighting arrangement to optimize plant growth.
The first thing you need to look for is any inconsistencies in the PAR meter readings. Check the readings for the lux level, quantum outputs and spectral range to ensure they fall within the recommended range for the specific plants you are growing.
If the readings show that the plants are receiving insufficient light, you will need to make some adjustments to the lighting arrangement. This could involve adjusting the light fixtures' placement to ensure uniform light distribution throughout the plant canopy.
You can also replace and upgrade the light bulb or entire fixture to increase the light intensity and quality. Upgrading to LED grow lights that provide a wider range of light spectrum can boost photosynthetic light and accelerate plant growth.
Step 8: Monitor Regularly to Ensure Optimal Growth Conditions
Your plants are dependent on the quality and intensity of the light provided to them for photosynthesis to take place. Therefore, it is important to regularly monitor your grow lights using a PAR meter to ensure that the light is reaching your plants at the right intensity and in the right spectrum range.
Final Thoughts on Measuring Grow Light With a Par Meter
Measuring grow light with a Par meter is a crucial aspect of indoor gardening that should not be overlooked. Consistent monitoring and adjustment using accurate tools like advanced Par light meters and quantum sensors can improve plant growth and yield, leading to a successful indoor gardening operation.