How Hydroponics is Helping End World Hunger
Imagine a world where barren lands, droughts, and poor soil fertility are no longer barriers to abundant food production. Picture urban rooftops, desert expanses, and basement gardens teeming with fresh produce. Sounds revolutionary, right? Enter hydroponics - the groundbreaking method of growing plants without soil.
This remarkable technology is not just about redefining farming; it's about reshaping our very approach to combating world hunger. Dive with us into the transformative world of hydroponics, and discover how this innovative method is bringing hope to millions, and propelling us towards a future where empty plates are a thing of the past.
Let's harness the potential of water-based farming, and take giant leaps in ensuring every mouth is fed!
Challenges to Addressing World Hunger
World hunger remains a pressing global issue that affects millions of people, particularly in impoverished regions. Traditional agriculture, which heavily relies on arable land and water sources, faces several challenges in meeting the ever-increasing food demand. Limited access to fresh produce, harsh environmental conditions, and the impact of natural disasters further aggravate the already precarious situation.
Food Insecurity
Food insecurity is a pressing issue that significantly contributes to global hunger. It refers to the lack of consistent access to safe, nutritious, and culturally appropriate food that meets dietary needs for an active and healthy life. Several factors contribute to food insecurity, including climate change, poverty, and transport and access issues.
Climate change is a major factor affecting food security. Rising temperatures, droughts, floods, and unpredictable weather patterns can result in reduced crop yields, affecting the availability and affordability of food. Impoverished communities, often reliant on subsistence farming, are particularly vulnerable to these climate-related challenges.
Poverty is another critical factor driving food insecurity. Limited financial resources restrict people's ability to purchase enough food, leading to malnutrition and hunger. Poverty also restricts access to education and healthcare, exacerbating these issues further.
Agricultural Land Use and Loss
Agricultural land use and loss have become critical issues in ensuring food security worldwide. The shrinking availability of viable farmland has led to challenges in meeting the growing demand for food. Various factors contribute to the lack of farmable land, including erosion, nutrient degradation, and urbanization.
Erosion, caused by factors like wind and water, results in the loss of valuable topsoil needed for plant growth. As soil erosion continues, it becomes increasingly difficult to cultivate crops and sustain agricultural productivity. Moreover, nutrient degradation occurs when excessive chemical fertilizer use or monocropping practices drain the soil of essential nutrients, rendering it less fertile.
Urbanization further exacerbates the scarcity of arable land. As cities expand, agricultural areas are converted into urban developments, leaving less space for traditional farming practices. The encroachment of urban areas onto farmable land diminishes the overall availability of land for food production.
These challenges in agricultural land use directly impact food security. As the demand for food increases, the limited availability of suitable farmland poses a significant threat to the global food supply. Alternative farming methods, like hydroponics, offer a solution by reducing reliance on agricultural land.
Water Requirements for Farming
Water is a critical resource in agriculture, playing a vital role in plant growth, nutrient absorption, and overall crop health. However, traditional farming methods often require vast amounts of water, leading to significant challenges in water availability and usage. This is where hydroponics, a soilless farming technique, can make a significant difference.
Traditional farming relies heavily on natural rainfall or extensive irrigation systems, resulting in high water requirements. This poses several challenges, including the depletion of freshwater sources, increased strain on water supplies, and vulnerability to droughts and changing climate patterns. With global food demand increasing and freshwater becoming scarce, these issues have become more pressing than ever.
Hydroponics offers a solution by dramatically reducing water consumption in farming. Hydroponic systems use controlled environments and closed systems, allowing for precise water delivery directly to the plant roots. Compared to traditional agriculture, hydroponics can save up to 90% of water requirements.
Feeding a Growing Population
Feeding a growing population poses significant challenges in the context of world hunger. The global population is projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, leading to an increasing demand for food. However, traditional agricultural practices face limitations such as the availability of arable land, unpredictable weather patterns, and escalating water requirements.
To ensure food security for all, innovative solutions are required. Hydroponic systems have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional farming methods. These systems allow for plant growth without soil, using nutrient-rich water solutions instead. By providing controlled environments, hydroponic farms can optimize crop yields and grow nutritious food all year round.
Unlike conventional agriculture, hydroponic farming minimizes the use of water and land. It eliminates the need for extensive irrigation, making it ideal for water-scarce regions. Moreover, hydroponic farms can be set up in urban centers, reducing the transportation time and costs associated with delivering fresh produce.
Hydroponics also offers opportunities for food production in harsh environments such as refugee camps or areas affected by natural disasters. By leveraging technology and optimization techniques, hydroponic farming can be implemented in closed systems using renewable energy sources like solar power.
The Benefits of Hydroponic Systems
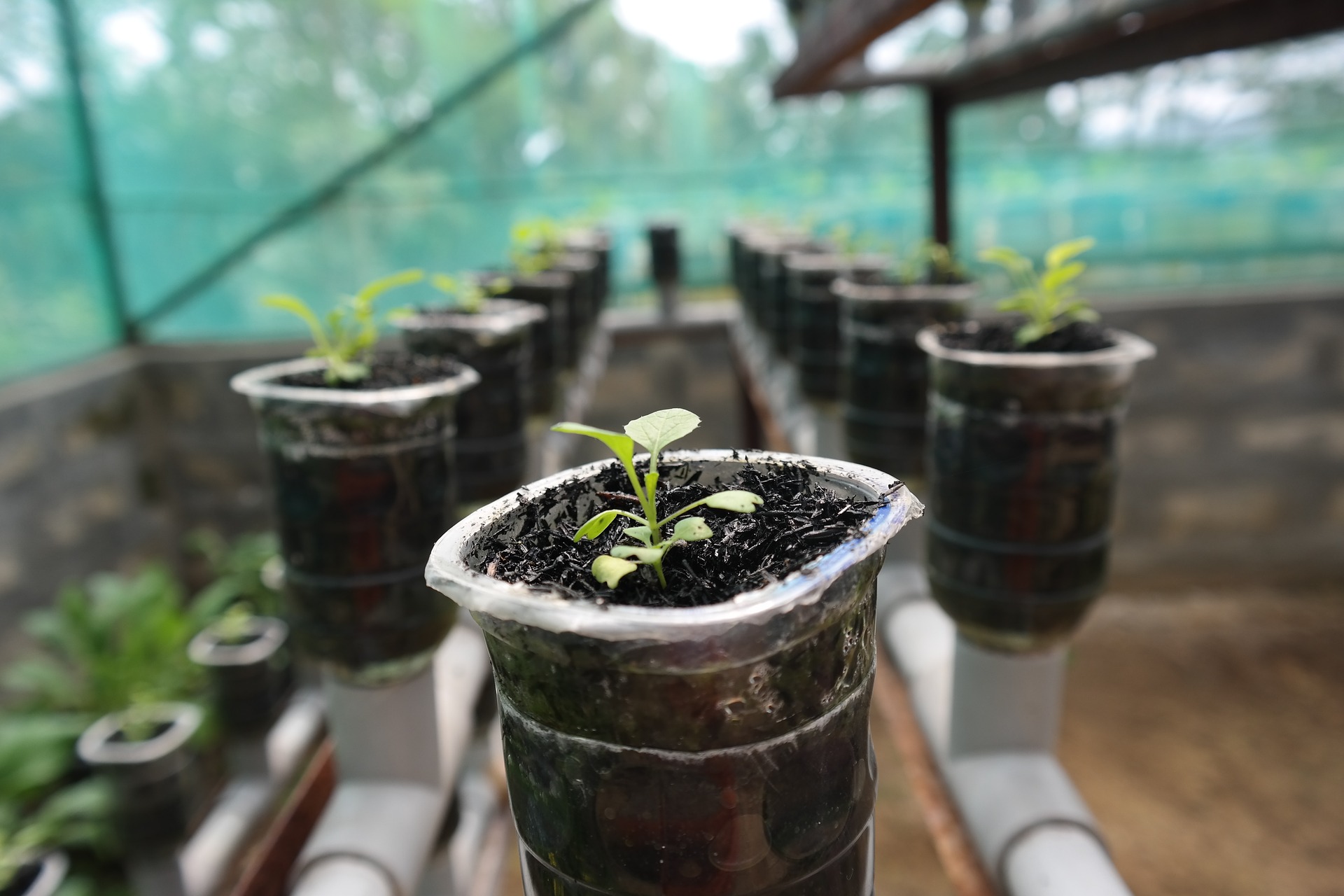

Hydroponic systems have emerged as a promising solution to address the global challenge of food insecurity and the ever-increasing demand for nutritious food. Unlike traditional agriculture, hydroponics allows for plant growth without the need for soil, instead using nutrient-rich water to nourish the hydroponic plants. This innovative approach to farming not only maximizes crop yields but also reduces the amount of agricultural land required, making it a viable option for urban environments with limited space.
Increased Crop Yields and Production Rates
Hydroponic systems offer an innovative solution to increase crop yields and production rates. Unlike traditional agriculture, which relies on soil, hydroponics allows plants to grow in nutrient-rich water solutions, resulting in faster and healthier plant growth.
One of the key factors contributing to increased crop yields in hydroponics is the controlled and monitored environment. By providing optimal conditions such as temperature, light, and nutrient levels, hydroponic systems maximize plant growth potential. This allows farmers to grow crops year-round, regardless of the outside climate or soil conditions. As a result, hydroponic farms have the ability to produce higher quantities of nutritious food.
Furthermore, hydroponic systems offer protection against external factors that can negatively impact crop production. By growing plants in closed systems, hydroponics prevents contamination from pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and herbicides. The controlled environment also shields plants from unpredictable weather changes, ensuring a stable production cycle.
Closed System for Indoor Farming and Vertical Farming

Closed system for indoor farming and vertical farming is a revolutionary approach to agriculture that enables year-round food production without being affected by climate change or adverse weather conditions. These systems utilize advanced technology and techniques to cultivate crops in a controlled environment, allowing for optimal growth and maximum yields.
One of the key advantages of a closed system is the elimination of the need for large-scale use of pesticides and herbicides. By creating a controlled environment, these systems provide a natural barrier against pests and diseases, reducing the reliance on harmful chemicals. This not only ensures the production of nutritious and chemical-free food but also contributes to a healthier environment.
Furthermore, closed systems for indoor farming and vertical farming promote sustainable urban living. In densely populated urban centers, where arable land is scarce, these systems allow for the cultivation of fresh produce in a sustainable manner. By utilizing vertical space and harnessing technologies such as solar energy, water recycling, and precise nutrient management, these systems create an efficient and environmentally friendly way to grow food.
Nutritious Produce with Reduced Pesticides
Hydroponics, a method of growing crops without soil, is revolutionizing the agricultural industry and offering innovative solutions to combat world hunger. One of the significant advantages of hydroponic systems is the production of highly nutritious produce with reduced pesticide use.
In hydroponics, plants receive essential nutrients directly in a carefully balanced nutrient solution. This allows the plants to uptake the nutrients more efficiently, leading to faster growth and healthier crops. As a result, hydroponic plants are often more nutrient-dense compared to those grown through traditional farming methods.
Furthermore, hydroponic systems are typically set up indoors or in controlled environments, minimizing the risk of pest infestations. The absence of soil in these systems eliminates the habitat where many pests thrive. Consequently, hydroponic crops are less prone to pest attacks, reducing the need for pesticides. As a result, the produce grown in hydroponic farms tends to have lower pesticide residues, making it safer and healthier for consumption.
Increased Access to Fresh Produce in Unfavorable Conditions
Hydroponics, a soil-less method of growing plants, has emerged as a powerful solution in tackling food insecurity and increasing access to fresh produce in unfavorable conditions.
Unlike traditional agriculture, hydroponic systems do not rely on soil conditions for plant growth. Instead, plants are cultivated in a nutrient-rich water solution, enabling them to thrive even in drought-prone areas or densely populated urban centers. This innovative technique allows for year-round production of high-quality crops, independent of the limitations imposed by arable land.
Hydroponic farming boasts numerous benefits. Firstly, it drastically reduces water consumption compared to conventional agriculture, making it an ideal choice for regions experiencing water scarcity. By utilizing closed systems and recirculating water, hydroponic farms require up to 90% less water than traditional farming methods. Additionally, since plant nutrition is carefully monitored and controlled, hydroponic crops tend to be more nutritious, offering a greater variety of vitamins and minerals to consumers.
More: How Does Hydroponics Work?
How Hydroponics Can Solve World Hunger Causes

Hydroponic farming has the potential to address the causes of world hunger by utilizing innovative techniques that can overcome the limitations of traditional agriculture. Here's how hydroponics can help solve these issues:
- Less water consumption: Hydroponic systems are designed to use up to 90% less water compared to traditional farming methods. This conservation of water resources is crucial for regions facing water scarcity or drought conditions, where traditional farming becomes increasingly challenging.
- Suitable for crowded cities and urban environments: Hydroponics can be implemented in vertical farms or indoor systems, allowing for food production in densely populated areas with limited space. This urban agriculture approach reduces dependence on agricultural land and transportation costs, ensuring fresh produce is readily available for urban populations.
- Elimination of erosion and soil degradation: Hydroponic farming eliminates the need for soil altogether. By growing plants hydroponically, the erosion of fertile topsoil and soil degradation caused by conventional farming practices can be minimized. This sustainable method helps preserve arable land for future generations.
- Direct access to water and nutrients: In hydroponic systems, plants are supplied with water and nutrients directly to their roots. This enables plants to grow faster and larger, leading to higher crop yields in a shorter time. This efficiency in nutrient delivery ensures a more predictable and consistent food supply, crucial in combating food insecurity.
| Aspect of Hydroponics | Contribution to Ending World Hunger |
| Water Efficiency | Uses up to 90% less water than traditional agriculture. |
| Space Saving | Allows for vertical farming, maximizing production in confined spaces like urban areas or even indoors. |
| Soilless Growth | Eliminates problems of soil-borne diseases, pests, and poor soil fertility. |
| Controlled Environment | Facilitates year-round growth regardless of external weather conditions, boosting food production rates. |
| Faster Growth Rate | Some hydroponic plants grow 50% faster than their soil-grown counterparts. |
| Reduced Transportation Costs | Localized hydroponic farms mean reduced food miles and fresher produce. |
| High Nutrient Content | Ability to control nutrients ensures high-quality, nutrient-rich produce. |
FAQs
How does hydroponics help address world hunger?
Hydroponics plays a crucial role in addressing world hunger by improving food production. It allows crops to be grown in any environment, including urban centers and harsh conditions, maximizing the use of limited arable land.
How does hydroponics improve crop yields?
Hydroponic systems provide optimal conditions for plant growth, such as precise nutrient delivery and controlled environments. This results in higher crop yields compared to traditional farming methods.
Can hydroponic plants provide nutritious food?
Yes, hydroponic crops are known to produce nutrient-dense and high-quality produce. By controlling the nutrient ratios in the growing solution, hydroponic farmers can ensure that plants receive all the essential nutrients necessary for their healthy growth.
Does hydroponics save water?
Hydroponics is highly efficient in water consumption. It requires up to 90% less water compared to conventional agriculture, as water is recirculated within closed systems, minimizing waste.
Does hydroponic farming require less water compared to conventional agriculture?
Yes, hydroponic farming uses up to 90% less water compared to traditional farming methods. Nutrient solutions in closed systems are recycled, minimizing water consumption and reducing pressure on existing water sources.
Can hydroponics be implemented in urban centers or areas with limited arable land?
Absolutely. Hydroponics is an ideal solution for urban farming as it enables crops to be grown vertically, utilizing small spaces efficiently. It is also an option for areas with limited arable land, such as refugee camps or regions affected by natural disasters.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydroponic farming offers a sustainable solution to food insecurity in urban areas, with the potential for higher crop yields. By eliminating the need for large amounts of arable land and utilizing vertical farming techniques, hydroponics allows for food production in urban centers where traditional agriculture is limited.
Partnerships between online supermarkets and hydroponic farms are also instrumental in driving down prices and increasing access to fresh produce. With a focus on sustainable food ethics, these collaborations contribute to reducing food insecurity by providing nutritious and affordable options to communities that may otherwise lack access to fresh food.
Furthermore, hydroponics has the potential to address the increasing demand for food production globally, particularly in areas prone to natural disasters or harsh environments such as refugee camps or Sub-Saharan Africa. By allowing plants to grow without soil and optimizing water consumption through closed systems, hydroponics offers a more efficient use of resources.
Overall, hydroponic farming presents an innovative approach to addressing food insecurity, offering the benefits of higher crop yields, reduced environmental impact, and increased access to healthy foods for communities in need. It holds immense potential for helping to end world hunger while promoting a more sustainable and resilient food system.